Öz
Giriş: Komissural lifler, serebral hemisferler arasında bilgi entegrasyonunu ve koordinasyonu sağlayan beyin ak madde yapısıdır. Komissural liflerden filogenetik olaran bilinen en eski liflerden olan posterior komissür, konsessual pupiller ışık refleksi gibi işlevlerde rol alır. Posterior komissürün anatomisi ve ilişkili yapıları literatürde kısıtlı sayıda çalışmada irdelenmiştir. Bu çalışmanın amacı, posterior komissürün mikrocerrahi anatomisini ilişkili olduğu diğer yapılarla beraber ak madde diseksiyonu ve traktografi yöntemleriyle ele almaktır.
Gereç ve Yöntem: Çalışmada Klingler tarafından önerilen yönteme uygun olarak beş adet postmortem insan beyin spesimeni üzerinde ak madde diseksiyonları gerçekleştirildi. Diseksiyonlar mikroskop altında mikrocerrahi tekniklerle yapılarak ve üç boyutlu fotoğraflama tekniği kullanılarak belgelendi. Posterior komissür ak madde lif diseksiyonu sonuçları 1065 deneğin difüzyon verilerini içeren bir şablondan elde edelin deterministik traktografi sonuçlarıyla karşılaştırıldı.
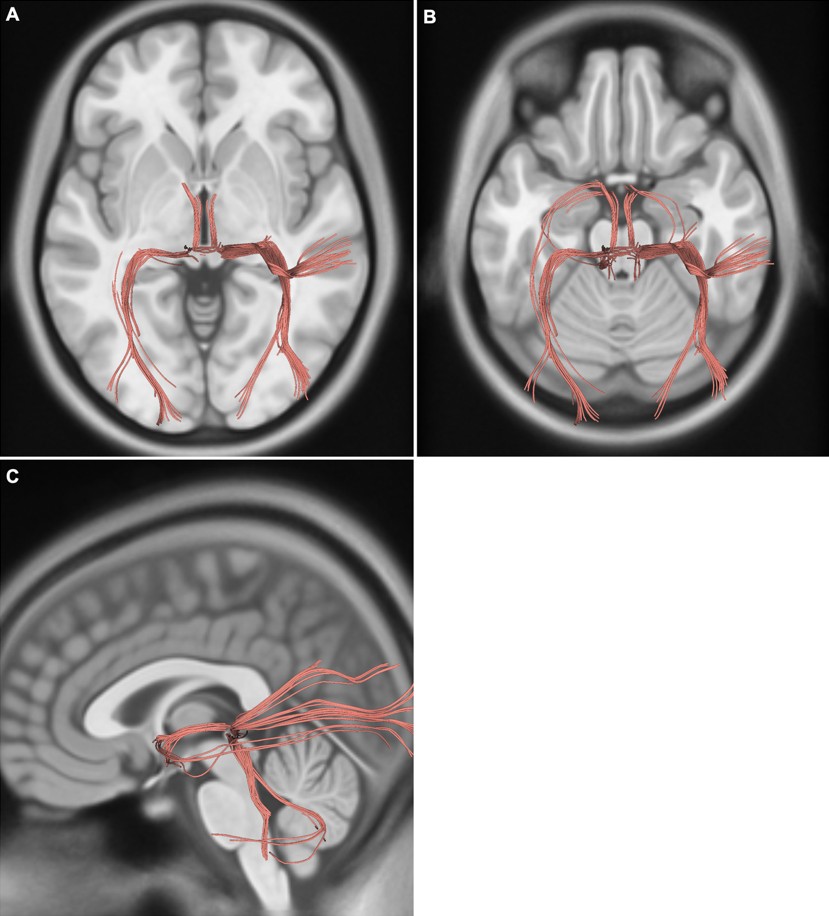
Bulgular: Diseksiyonlar sonucunda posterior komissürün anatomik olarak kuadrigeminal korpora, pineal gland, habenular komissür ve stria medullaris talami gibi yapılarla yakın komşuluğu tanımlanmıştır. Liflerin inferiorda superior kollikulus, posteriorda ise habenular komissürle devamlılık gösterdiği görülmüştür. Traktografi analizleri posterior komissür liflerinin talamus, tektal alan, superior kollikulus, beyin sapı ve serebellumla bağlantılı olduğunu ortaya koymuştur.
Tartışma: Posterior komissür, yalnızca pupiller refleksle sınırlı kalmayıp, beyin sapı ve serebellumla olan bağlantılarıyla daha geniş bir fonksiyonel ağa sahiptir. Bu lifler, pretektal alan ve çeşitli mezensefalik çekirdeklerle de ilişkili olup, ışık reflekslerinden vestibüler sistemle bağlantılara kadar çeşitli görevler üstlenir. Çalışmamız posterior komissürün hem anatomik hem de fonksiyonel yönlerini ayrıntılı olarak ortaya koyan nadir anatomik çalışmalardan biridir.
Anahtar Kelimeler: posterior komissür, komissural lifler, lif diseksiyonu, difüzyon tensör görüntüleme
Giriş
Beyinin ak maddesi spinal kord ve beyin sapı çekirdeklerinden kortekse uzanan projeksiyon lifleri, aynı hemisfer içerisindeki kortikal yapıları birbirine bağlayan assosiasyon lifleri ve her iki hemisferi birbirine bağlayan komissural liflerden oluşur.1,2 Komissural lifler hemisferler arasındaki bilgi koordinasyonu, entegrasyon ve vücut koordinasyonunun sağlanmasında görev alır.3 Félix Vicq d’Azyr (1748–1794) aynı hemisferin farklı bölgeleri arasında uzanan liflerin aksine hemisferler arasındaki bağlantılar (komissür) kavramını ortaya koyarak ilk kez anterior ve posterior komissürleri tanımladı.4,5
Ana komissural lifler bağlandıkları beyin yapılarına göre telensefalik ve diensefalik komissürler olarak sınıflandırılır. Diensefalik komissürleri posterior ve habenular komissürler oluşturur. Habenular ve posterior komissürler, pretektal plağın diensefalik kısmında gelişir ve epifizyal evajinasyonla ayrılır.5 Posterior komissür mezensefalonla kaudalde bitişiktir ve inferior pineal laminada yer alır. Posterior komissür lifleri pretektal nukleusları birbirine bağlayarak pupiller ışık refleksinin uyumuna katkı sağlar. Habenular komissür ise stria medullaris talami ve habenulo-interpedinküler traktuslarla beraber dorsal diensefalik limbik sistemin iletisine katkı sağlar.5 Melatonin sentez ve salgılamasında görev yapan pineal gland habenular ve posterior komissürler arasındaki diensefalon tavanının median çıkıntısından gelişirek pineal sap aracılığıyla kaudal diensefalona bağlanır.5 Posterior komissür anatomisi ve bağlantıları literatürde kısıtlı sayıda çalışmada incelenmiş olup, yakın ilişki içerisinde olduğu yapılarla beraber ayrıntılı olarak anlatılmamıştır. Bu çalışmanın amacı, posterior komissür bağlantıları ile yakın komşuluklarının ayrıntılı mikrocerrahi anatomisini ak madde lif diseksiyonu ve traktografi yöntemleri ile göstermektir.
Gereç ve Yöntem
Ak madde diseksiyonu için 5 adet postmortem insan beyin spesimeni, Klingler metoduna uygun olarak %10’luk formalin solüsyonunda 3 hafta bekletildi. Araknoid mater, pia mater ve vasküler yapılar uzaklaştırıldıktan sonra -160C’de donduruldu. Ardından çeşme suyunda çözülerek ak madde diseksiyonuna başlandı. Spesimenler diseksiyonlar arasında %70’lik alkol solüsyonunda korundu.6,7 Ak madde diseksiyonu Zeiss OPMI Pico mikroskop (Carl Zeiss AG, Oberkochen, Germany) altında x4 ve x40 büyütmede, mikrocerrahi el aletleri (dişsiz penset, Rhoton dissektörü, metal spatula ve mikrohook) kullanılarak yapıldı. Her aşama Canon Dijital SLR fotoğraf makinesi, 100 mm’lik makro lens, ring flaş ve tripot kullanılarak Shimizu ve ark. tarafından tariflenen üç boyutlu fotoğraflama tekniği kullanılarak fotoğraflandı.8
Fiber diseksiyon sonuçlarının bütünlüğünü değerlendirmek için human connectome project normal deneklerden elde edilen manyetik rezonans görüntüleme difüzyon tensor traktografisi kullanıldı. Posterior komissür traktusu DSI Studio’da (http://dsi-studio.labsolver.org) yapılan analizlerle 1065 deneğin difüzyon verilerini içeren bir şablon üzerinde deterministik traktografi kullanılarak üretildi. 9,10 Görüntüleme protokolünün ve ön işleme adımlarının tam açıklaması human connectome project web sitesinde (https://www.humanconnectome.org) mevcuttur. Traktografi parametreleri minimum fraksiyonel anizotropi 0.15, adım boyutu 0 mm, minimum uzunluk 10 mm ve maksimum uzunluk 200 mm’dir.11
Bulgular
Vasküler yapılar ve araknoid membran kaldırıldıktan sonra beyin medial yüzeyinin önemli anatomik nirengi noktaları tanımlanarak gösterildi (Şekil 1A).
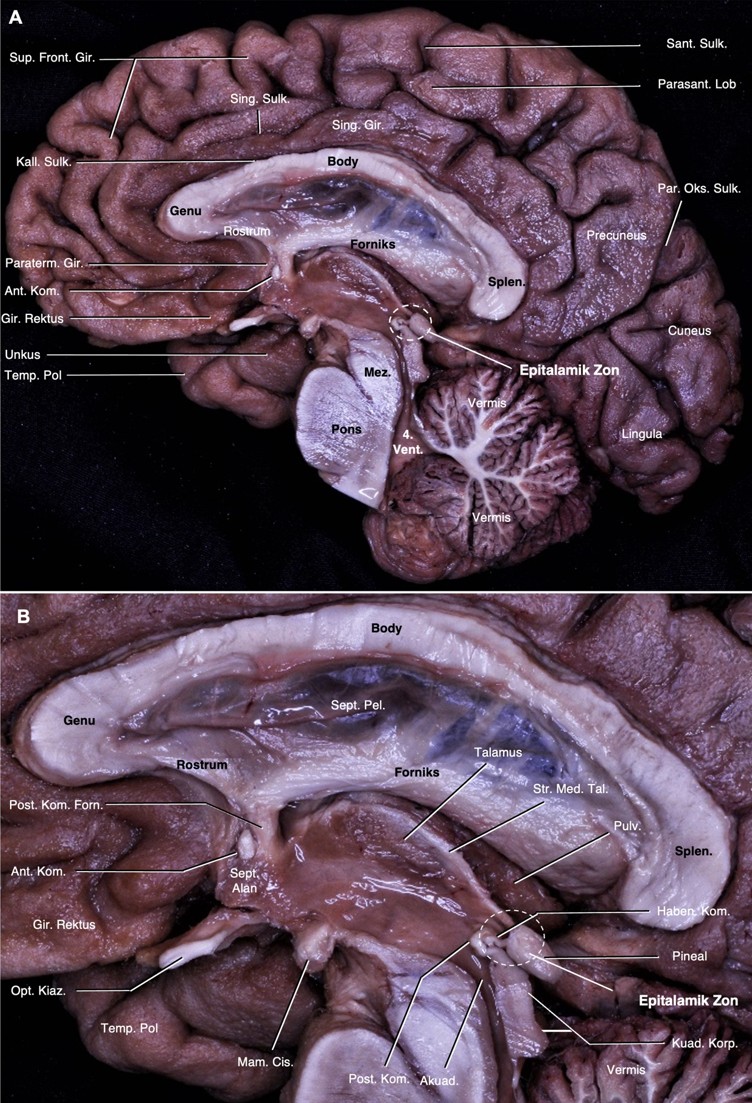
Beyin medial yüzeyinde serebral komissural lifler tanımlandı. Serebral komissural liflerin en büyüğü olan korpus kallozum, orta hatta, serebral hemisferlerin arasındaki interhemisferik sulkusun tabanına yerleşir. Korpus kallozum indusium griseum ile örtülür. Kallozal sulkus ile tamamen çevrelendiği singulat girustan ayrılır (Şekil 1A).1 Korpus kallozumun splenium kısmının anterioru ile rostrum kısmının posterioru arasında ve 3. ventrikül superiorunda forniksin kolumnası seyreder. 3. ventrikül anteriorunda, septal alanın arkasında forniks prekomissural ve postkomissural olarak ikiye ayrılır. Anterior komissür bu iki yapının arasında yer alır. Anterior komissürün anteriorunda septal alan ve prekomissural forniks, inferiorunda hipotalamus ve optik kiazma, posteriorunda ise postkomissural forniks izlenir. Postkomissural forniksin arkasında habenular kompleksin bir parçası olan stria medullaris talami talamusun medial yüzeyinde ‘epitalamik zon’a (habenular komissür ve pineal gland) doğru seyreder. 3. ventrikül posteriorunda habenular komissür ve pineal glandın yer aldığı epitalamik zon yer alır. Burası serebral akuaduktusun üst dorsal yüzeyinde ve kuadrigeminal korporanın superiorunda yer alan diensefalik alanı oluşturur. Posterior komissür epitalamik zon ile iç içedir ve hemen anteroinferiorunda yerleşim gösterir. 3. ventrikül arka duvarını oluşturan yapıların en önde yer alanıdır (Şekil 1).
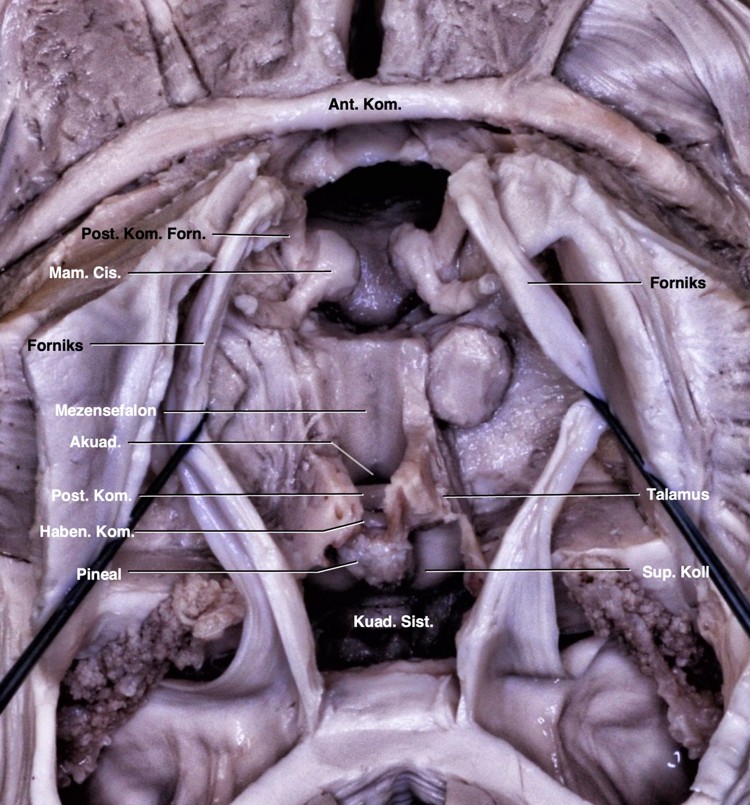
Posterior komissür mesensefalon ile diensefalon arasındaki sınırın dorsalini oluşturur (Şekil 1, 2). Posterior komissürün inferiorunda kuadrigeminal korpora ve akuaduktus, anteriorunda 3. ventrikül boşluğu, superiorunda stria medullaris talami, posterosuperiorunda habenular komissür ve posteriorunda pineal glandın yer aldığı kuadrigeminal sisterna yer alır. Kadavramızda posterior komissür liflerinin inferiorda superior komissürle ve posteriorda habenular komissürle devamlılık halinde olduğu gösterildi (Şekil 1B). Pineal glandın altında yer alan pineal reses rostral olarak habenular komissür ve kaudal olarak posterior komissür ile sınırlandı. Orta hatta talamusun alt sınırı laterale doğru dönüş gösterdiği yer anterior komissür dorsali ile posterior komissür ventralinden geçen ‘Talairach’ düzlemine denk geldiğini gösterdik (Şekil 2).
Difüzyon tensor traktografisi çalışmamızda posterior komissürden geçen liflerin talamus, habenular kompleks, tektal alan ve superior kollikuluslar aracılığıyla beyin sapı ve serebellum ile ilişkili olduğunu göstermekteyiz (Şekil 3).
Tartışma
Her iki yarım kürenin orta hatta birbirine bağlanmasıni sağlayan komissural liflerden telensefalik ve diensefalik komissürleri korpus kallozum, anterior komissür, hipokampal komissür, posterior komissür ve habenular komissür oluşturur.5 Posterior komissür filogenetik olarak bilinen en eski komisural liflerden biri olup pretektal çekirdekleri bağlayarak pupil refleksinde rol oynar.5 Ayrıca posterior komissür akuaduktusun üzerindeki merkezi gri maddede yer alan posterior komissürün çekirdeği olan Darkschewitsch çekirdeği, Bechterew çekirdeği, aksesuar optik çekirdeği, subkomissural organ ve okülomotor fasikülünün superiorunda yer alan Cajal interstisyel çekirdeği gibi çeşitli çekirdeklerle ilişkilidir.5,12 Bu çekirdeklerle anatomik olarak ilişkisi halen karmaşıktır.
Pretektal alan superior kollikulusun hemen rostralinde yer alır. Retinadan gelen bir kısım lifler posterior komissürde çapraz yaparak pretektal alandaki pretektal olivar çekirdeklerde sonlanır ve konsensual ışık refleksinde görev alır. Ayrıca posterior komissür çekirdeği bazen pretektumda yerleşimlidir. Posterior komissür ayrıca aksesuar optik sistemin terminal çekirdeklerinden, beyin sapı ve serebellumun afferent sistemlerinden de komissural lifler içerir. Aksesuar optik sistem rostral mezensefalonda görsel çevrenin küresel hareketlerinin hızı ve yönünü kaydetmeyi sağlayan, Cajal’ın interstisyel, Darkschewitsch ve Bechterew çekirdeklerine projeksiyon yapan çekirdeklerden oluşur. Bu çekirdekler iki taraflı olarak posterior komissür lifleri ile çaprazlaşır.5,13 Anatomik diseksiyonlarımızda pretektal çekirdekleri gösterememiş olsak da posterior komissürün iki taraflı pretektal alanla yakın ilişkide olduğunu gösteriyoruz (Şekil 1).
Epandimal hücrelerden oluşan subkomissural organ yapılan hayvan deneylerinde 3. ventrikül dorsal kısmını oluşturur ve embriyonik olarak posterior komissürün hemen ventralinde bulunan nöroepitelyal hücrelerin dorsal orta hat tabakasından oluşur. Işık ve elektron mikroskopi çalışmalarında bu nöroepitelyal yapının ventrikül içindeki beyin omurilik sıvısına bir salgı salgıladığı ve bu salgının Reissner lifi olarak bilinen filamentöz bir yapı oluşturmak üzere bir araya geldiği gösterilmiştir.14 Reissner lifinin beyin omurulik sıvısı hemodinamiğinde görev aldığı ve buna bağlı olarak subkortikal organın anormal gelişimi veya işlev bozukluğunun hidrosefali ile ilişkili olduğu bildirilmiştir.15 Ayrıca posterior komissürün gelişimi olmak üzere özellikle de embriyogenez esnasında nörogenez ve akson rehberliğinde rol oynadığını belirten çalışmalar mevcutur.16,17 Literatüre insanlarda henüz anatomik olarak gösterilemeyen subkomissural organı çalışmamızda posterior komissürden ayırt ederek tanımlayamadık.
3. ventrikül beyinin merkezinde, korpus kallozum ve hipokampal komissürün altında, mesensefalonun üstünde ve her iki talamusun arasında yer alır. Tabanı önde optik kiazmadan akuaduktusa, anterior duvarı optik kiazmadan anterior komissüren geçerek foramen monroya, tavanı önde foramen monrodan arkada suprapineal girintiye hafif yukarı doğru kemer şeklinde ve posterior duvarı suprapineal girintiden akuaduktusa uzanır. Habenular komissür, pineal gland, pineal girinti ve posterior komissür arka duvarda yer alır. Tavanın ön kısmında foramen monrodan habenular komissüre doğru talamusun superomedial sınırı boyunca internal serebral venlerin seyrettiği velum interpositumu işaretleyen stria medullaris talami uzanır.1 Kuadrigeminal sisterna pineal glandın etrafını çevreler. Anteriordan kuadrigeminal plaka ve pineal glandla, laterallerde pulvinar ve okspital lobun inferomedial yüzeyiyle, superiorda spleniumla ve inferiorda serebellumun tentoriyal yüzeyi ile sınırlanan subaraknoid boşluktur. 3. ventrikülün suprapineal girintisi, pineal glandın superiorundan kuadrigeminal sisternaya doğru olan çıkıntıdır.18,19 Çalışmamızda 3. ventrikülün tüm sınırlarını tanımladık. Posterior ve habenular komissürler 3. ventrikülün posterior duvarı ve kuadrigeminal sisternanın anterior duvarında yer almaktaydı. Pineal girinti, rostralde habenular komissür ve kaudalde posterior komissür ile sınırlanmıştı. Ayrıca stria medullaris talami habenular komissür ile septal alan arasında seyretmekteydi (Şekil 1).
‘Talairach düzlemi’ anterior komissürün dorsali ve posterior komissürün ventralinde geçen düzlemdir. Bu düzlem beyin görüntüleme çalışmalarında kullanılır.20 Talairach düzlemine dik olarak posterior komissürden geçen ‘vertikal posterior komissür çizgisi’ suplementer motor alan ile pre-suplementer motor alanın birbirinden ayrıldığı hattır. Çalışmamızda hem sagital hem de aksiyal yönelimde aynı anda anterior ve posterior komissürleri göstererek talairach düzlemi ve dikey posterior komissür hatlarından geçen anatomik yapıları gösterdik.
Posterior komissür pineal bölgenin tümörlerinde önemli bir landmark noktası olarak kullanılabilir. Hatta pineal bölgenin nadir bir tümörü olan papiller tümör pineal glandtan ziyade posterior komissürün hemen ventralinde yer alan subkomissural organın ependimositlerinden oluşan nöroepitalyal kökenli tümörleridir.20 Posterior komissür ve subkomissural organ ilişkisinin bilenmesi ve ayrıca bu lezyonların pineal gland tümörlerinden ayrılması beyin cerrahları için önem arz etmektedir.20,21
Literatürde komissural liflerin anatomi ve fonksiyonlarını içeren anatomi ve traktografi çalışmaları mevcut olmakla birlikte, insan kadavrasında posterior komissürü temel alan çalışmalara çok rastlanmamışır.22,23 Bu anatomik çalışmada, posterior komissür liflerinin seyrini, anatomik önemini ve komşu yapılarla ilişkilerini gösterek posterior komissür ilişkili çekirdekleri fonksiyonları ışığında tartıştık.
Etik kurul onayı
Bu çalışma, uygun kurumsal protokollerle elde edilen postmortem beyin örnekleri ve anonimleştirilmiş açık erişimli veriler kullanılarak gerçekleştirildiğinden, etik kurul onayı gerektirmemektedir.
Yazarlık katkısı
Çalışma konsepti ve tasarımı: OB, ŞSB; veri toplama: OB, MAE; sonuçların analizi ve yorumlanması: OB, ŞSB; makaleyi hazırlama: OB, ŞSB. Yazar(lar) sonuçları gözden geçirmiş ve makalenin son halini onaylamıştır.
Finansman
Yazar(lar), çalışmanın herhangi bir finansal destek almadığını beyan etmiştir.
Çıkar çatışması
Yazar(lar) herhangi bir çıkar çatışması olmadığını beyan etmiştir.
Kaynakça
- Rhoton Jr AL. The cerebrum. Neurosurgery 2007; 61. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.NEU.0000255490.88321.CE
- Schmahmann J, Pandya D. Fiber pathways of the brain. New York: Oxford University Press; 2006. https://doi.org/10.1093/acprof:oso/9780195104233.001.0001
- Ozdemir NG. The anatomy of the posterior commissure. Turkish Neurosurgery 2015; 25(6): 837-843. https://doi.org/10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.12122-14.2
- Clarke E, O'Malley CD. The human brain and spinal cord: a historical study illustrated by writings from antiquity to the twentieth century. San Francisco: Norman Publishing; 1996.
- Nieuwenhuys R, Voogd J, Van Huijzen C. The human central nervous system: a synopsis and atlas. Springer Science & Business Media; 2007. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-34686-9
- Klingler J. Erleichterung der makrokopischen Präparation des Gehirns durch den Gefrierprozess. Orell Füssli; 1935.
- Agrawal A, Kapfhammer JP, Kress A, et al. Josef Klingler's models of white matter tracts: influences on neuroanatomy, neurosurgery, and neuroimaging. Neurosurgery 2011; 69: 238-252. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0b013e318214ab79
- Shimizu S, Tanaka R, Rhoton AL, et al. Anatomic dissection and classic three-dimensional documentation: a unit of education for neurosurgical anatomy revisited. Neurosurgery 2006; 58: E1000. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.NEU.0000210247.37628.43
- Yeh FC, Tseng WYI. NTU-90: a high angular resolution brain atlas constructed by q-space diffeomorphic reconstruction. Neuroimage 2011; 58: 91-99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.06.021
- Yeh FC, Wedeen VJ, Tseng WYI. Generalized q-sampling imaging. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 2010; 29: 1626-1635. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2010.2045126
- Yeh FC, Panesar S, Fernandes D, et al. Population-averaged atlas of the macroscale human structural connectome and its network topology. Neuroimage 2018; 178: 57-68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2018.05.027
- Keene ML. The connexions of the posterior commissure: a study of its development and myelination in the human foetus and young infant, of its phylogenetic development, and of degenerative changes resulting from certain experimental lesions. Journal of Anatomy 1938; 72(Pt 4): 488-501.
- Young MJ, Lund RD. The anatomical substrates subserving the pupillary light reflex in rats: origin of the consensual pupillary response. Neuroscience 1994; 62: 481-496. https://doi.org/10.1016/0306-4522(94)90381-6
- Gilbert TT, Olopade FE, Ladagu AD, et al. Microscopic anatomy of the subcommissural organ in the brain of the adult greater cane rat (Rodentia: Thryonomyidae). Anat Histol Embryol 2024; 53: e12990. https://doi.org/10.1111/ahe.12990
- Ortloff AR, Vío K, Guerra M, et al. Role of the subcommissural organ in the pathogenesis of congenital hydrocephalus in the HTx rat. Cell Tissue Res 2013; 352: 707-725. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-013-1615-9
- Grondona JM, Hoyo-Becerra C, Visser R, Fernández-Llebrez P, López-Ávalos MD. The subcommissural organ and the development of the posterior commissure. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 2012; 296: 63-137. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-394307-1.00002-3
- Corales LG, Inada H, Hiraoka K, et al. The subcommissural organ maintains features of neuroepithelial cells in the adult mouse. J Anat 2022; 241: 820-830. https://doi.org/10.1111/joa.13709
- Rhoton AL. Tentorial incisura. Neurosurgery 2000; 47: S131-S153. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006123-200009001-00015
- Rhoton Jr AL. The posterior cranial fossa: microsurgical anatomy and surgical approaches. Neurosurgery 2000; 47(suppl_3): S5-S6. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006123-200009001-00005
- Jouvet A, Fauchon F, Liberski P, et al. Papillary tumor of the pineal region. Am J Surg Pathol 2003; 27: 505-512. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000478-200304000-00011
- Kennedy G, Degueure A, Dai M, Cuevas-Ocampo A, Arevalo O, Cuevas-Ocampo AK. An unusual finding: papillary tumor of the pineal region. Cureus 2023; 15(2): e34725. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.34725
- Vilela-Filho O, Freitas ELA, Goulart LC, Lino-Filho AM, Carneiro R, Fernandes-Santos B. 7T magnetic resonance imaging probabilistic tractography-based evidence of decussation of the fibers between the lateral geniculate nucleus and the primary visual area. World Neurosurg 2024; 188: e555-e560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2024.05.152
- Dauleac C, Mertens P, Frindel C, Jacquesson T, Cotton F. Atlas-guided brain projection tracts: from regions of interest to tractography 3D rendering. J Anat 2025; 246: 732-744. https://doi.org/10.1111/joa.14120
Telif hakkı ve lisans
Telif hakkı © 2025 Yazar(lar). Açık erişimli bu makale, orijinal çalışmaya uygun şekilde atıfta bulunulması koşuluyla, herhangi bir ortamda veya formatta sınırsız kullanım, dağıtım ve çoğaltmaya izin veren Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) altında dağıtılmıştır.